Laser has been applied in teaching, military as well as industrial production. Laser cutting machine is one of the applications. It can be used in both metal and non-metal cutting, Melting surface material by laser beam. This article will discuss the work theory of laser cutting machine.
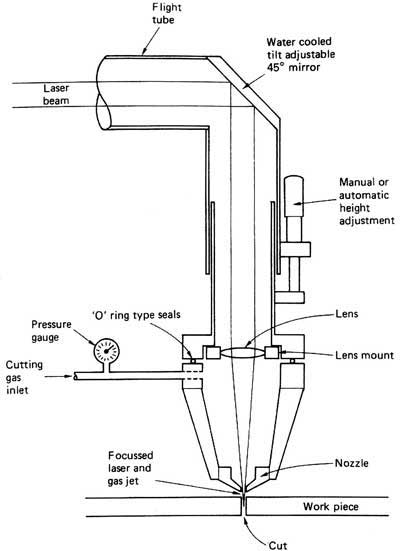
Introduction on the work theory of laser cutting machine.
Laser cutting machine adopts the energy released on the time when laser beam irradiate metal surface. The metal is melt by laser and sinter is blow away by gas. Because laser power is highly focused, only a very little heat effects the other part of metal plate and causes a little or no deformation. Laser can cut any complex shape precisely, which needs no further processing.
Laser source is generally CO2 laser beam high power isolator with operating power of 500~5000W. The power is even lower than that of many household electric heater, and because of lenses and reflectors, laser beams are focused in a very small bit of area. Highly focused energy heat the area quickly and makes the metal plate melted.
Laser cutting machine can cut stainless steal of thickness less than 16mm; when adding oxygen in laser beam, the cutting thickness is 8~10mm but it will generate a thin oxidation film in the cut surface. The maximum thickness is 16mm which leads to larger cutting deviation on the size of components.
Since the advent of laser, numerous laser products have been developed, such as laser printer, laser cosmetic instrument, laser marker, laser cutting machine etc. Due to its late start in China, the laser technology in China is greatly behind the developed countries. Although Chinese manufacturers can produce plenty of laser products, some key parts such as laser tube, driving motor, galvanometer and focus lens are imported products. This leads to an increase on cost thus an increase on consumer’s payment.
In recent years, domestic research and production of laser products become closer to advanced overseas products with the progress of laser technology in China. Some aspects are even superior to products abroad, which has a leading role in market because of the advantages of price. Overseas products have absolute predominance in precision machining for its quality on stability and endurance.
Work theory of laser cutting machine
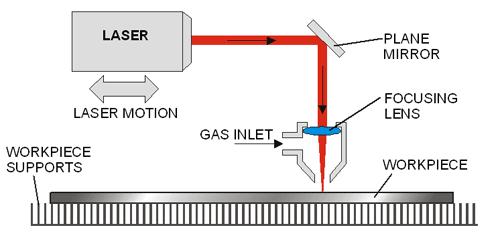
Laser tube is the core part of laser cutting machine. So, below is an introduction of the most popular laser tube. CO2 laser tube.
Laser tube is composed of hard glasses, so it is fragile. It adopts layer of sleeve construction with discharge tube in the most inside layer. However, the diameter of discharge tube is thicker than laser tube, diffraction between the thickness of discharge tube and the size of flare is in direct ratio; the length of tube is in proportion to output power of discharge tube. Laser tube generates a large quantity of heat in the operation of laser cutting machine, which influences the normal work. So cold water machine is needed to cool laser tube, ensuring constant temperature for successful running.
Cutting features of laser cutting machine
Advantages of laser cutting:
One — high efficiency
Laser cutting machine is always connected to several numerically-controlled rotary tables to achieve numerical controlled cutting. It only needs to change the NC program to adjust to components of different shapes, which can make 2D cutting as well as 3D cutting.
Two — high speed
When cutting low carbon steel sheets of 2mm thickness, the speed of 1200W laser cutting is 600cmmin; when it is 5mm thick polypropylene resin plate, the cutting speed is 1200cmmin. The material needs no clamping fix in laser cutting process.
Three — high quality cutting
Laser cutting features thin kerf. The two sides of kerf are parallel and the kerf is vertical to the surface. The cutting precision can reach to ±0.05mm. The cutting surface is clean and nice, with roughness of tens of microns. The cut components can even come into use directly without further machining. After laser cutting, the heat effected area is very small and material near to kerf has not been affected, making little deformation, high cutting precicion and perfect geometrical shape
Four — non-contact cutting
Laser cutting is non-contact cutting, which means no tool wear problem. When processing different shapes, there is no need to change tools, the only way is to alter the output parameter of laser. The whole laser cutting process features low noise, little vibration and little pollution.
Five — various cutting material
Compared to oxyacetylene cutting and plasma cutting, laser cutting can be applied on more materials, including metal and non-metal, metal matrix and non-metallic matrix composite, leather, wood as well as fibers.
About DK Photonics
DK Photonics – www.dkphotonics.com specializes in designing and manufacturing of high quality optical passive components mainly for fiber laser applications such as 1064nm high power isolator, Cladding Power Stripper, Multimode High Power Isolator, pump signal combiner,1064nm Band-pass Filter,(6+1)X1 Pump and Signal Combiner, PM Circulator, PM Isolator, optical Coupler. More information, please contact us.