Technological parameter of laser welding:
(1) Power density
Power density is one of the key parameters in laser processing. When the power density is relatively high, the surface would be heated to boiling point in microseconds, thus generate mass vaporization. As a result, high power density is good for material removal processing such as punching, cutting and carving. When the power density is relatively low, it would take some microseconds to meet the boiling point, the bottom can reach the melting point before vaporization occurs, thus a good melt welding is successfully formed. So the power density ranges from 104~106W/cm2 in conductive laser welding.
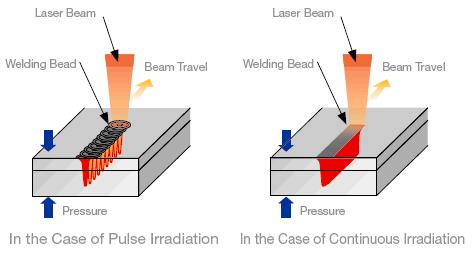
(2) Laser pulse shape
Laser pulse shape is an important question in laser welding, especially for foil welding. When high strength laser beam reaches the material surface, 60~98% of the laser energy will be lost by reflection and the reflectivity is changeable by the temperature of the material surface. The reflectivity of metal can vary greatly in a laser pulse period.
(3) Laser pulse width
Laser pulse width is an important parameter to distinguish material removal and material melting; it is also a key parameter to decide the cost and volume of processing equipment.
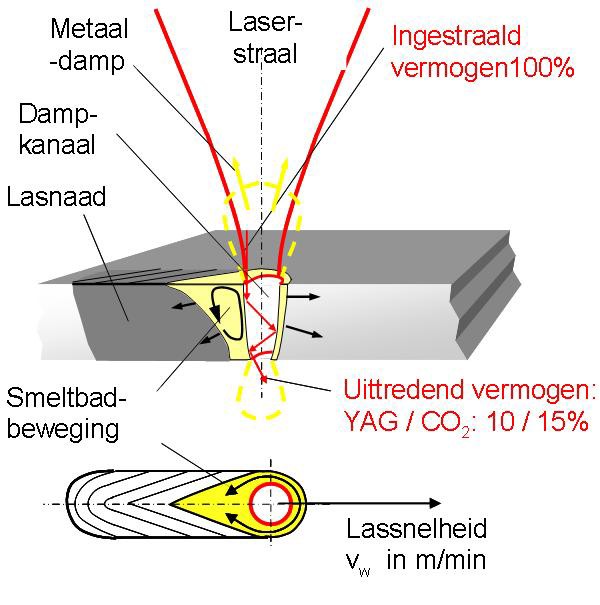
(4) Influence of defocusing amount on weld quality
There are two ways of defocus: positive defocus and negative defocus. It is positive defocus when focal plane is above the workpieces, vise versa. According to geometry optical theory, when positive and negative defocusing plane equals to welding plane, the power densities are almost the same in the corresponding panels, but the actual laser pools have different forms. It can achieve larger depth of fusion when it is negative defocus.
Application field of laser welding
Laser welding machine has wide application in manufacturing industry, powder metallurgy field, automobile industry, electronics and some other fields.
Source : demarlaser
Application of laser welding in automobile industry
Volkswagen AG has adopted laser welding in car roof of brands like AudiA6, GolfA4 and Passat. BMW and GM have used laser welding in top of the car frame while Mercedes-Benz has applied laser welding in drive disk assembly. Except for laser welding, other laser technologies have be applied as well. Companies like Volkswagen GM, Benz and Nissan have used laser to cut covering parts while FIAT and Toyota have adopted laser for coating engine exhaust valve; Volkswagen has used laser for surface hardening on engine camshaft. Domestic vehicle models like Passat, Polo, Touran, Audi, Dongfeng Peugeot and Focus have adopted laser welding technology.
Independent automobile brands like Brilliance, Chery and Geely have adopted laser welding as well.
Improvement and development of new laser welding technology
Laser welding technology is continuously developing along with the progress of the time. The following three technologies can help expanding laser’s application scop and enhancing the automatic control level of laser welding.
- filler wire laser welding
Laser welding generally doesn’t fill wires but has high requirement on assembling clearance, which is hard to be guaranteed thus limits the application scope. Filler wire laser welding method has lower requirement on assembling clearance. For example, if the aluminum alloy plate is of 2 mm’s thickness, the clearance must be zero for a good shaping. When adopting φ1.6mm welding wire as filler metal, it can form good shape even the clearance is 1.0 mm. Besides, filler wire can be used for adjusting chemical components and multi-layer welding on thick board.
- Beam rotation laser welding
By the adoption of laser beam rotation laser welding methods, demands on welding assembly and beam centering are reduced greatly.
- On-line detection and control of laser welding quality
It is becoming a hot researching topic on detecting laser welding process by using plasma such as light, sound and electric charge; some researches have achieved closed-loop control.
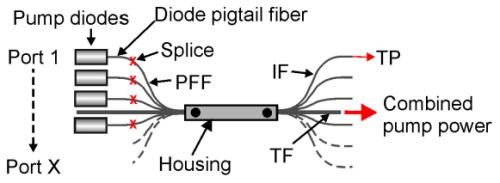
DK Photonics – www.dkphotonics.com specializes in designing and manufacturing of high quality optical passive components mainly for fiber laser applications such as 1064nm high power isolator, Cladding Power Stripper, Multimode High Power Isolator, pump combiner,1064nm Band-pass Filter,(6+1)X1 Pump and Signal Combiner, PM Circulator, PM Isolator, optical Coupler. More information, please contact us.