Optical fiber communication has revolutionized the way data is transmitted over long distances, enabling high-speed internet, telecommunication, and more. Among the many components involved, CWDM Mux/Demux plays a crucial role in maximizing the efficiency of optical networks. Let’s delve into what CWDM Mux/Demux is and how it works:
What is CWDM Mux/Demux?
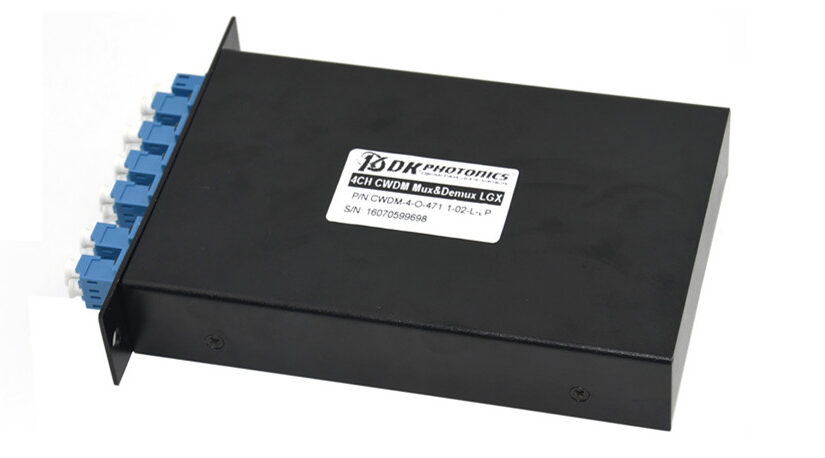
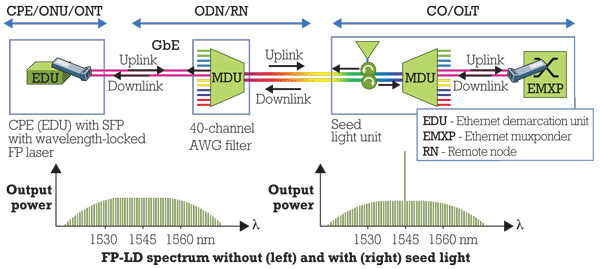
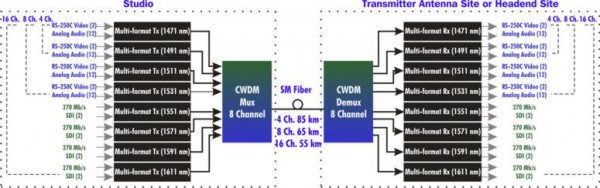
CWDM stands for Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexing. CWDM Mux/Demux is a passive optical component used in fiber optic communication networks to combine multiple optical signals of different wavelengths onto a single fiber or to separate these signals back into individual wavelengths.
How Does CWDM Mux/Demux Work?
CWDM Mux/Demux operates based on the principle of wavelength division multiplexing (WDM). It consists of multiple input and output ports, each corresponding to a specific wavelength channel. The Mux (Multiplexer) combines several incoming optical signals with different wavelengths into a single fiber, while the Demux (Demultiplexer) separates these signals back into individual channels at the receiving end.
Benefits of CWDM Mux/Demux:
- Increased Bandwidth: By utilizing different wavelengths, CWDM Mux/Demux allows for the simultaneous transmission of multiple data streams over a single fiber, effectively increasing the bandwidth capacity of the network.
- Cost-Effective Solution: CWDM technology is more cost-effective compared to Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM), making it ideal for applications where high channel counts are not required.
- Simplified Network Architecture: CWDM Mux/Demux simplifies network architecture by reducing the number of fibers needed for transmission, thus minimizing installation complexity and maintenance costs.
Applications of CWDM Mux/Demux:
- Telecommunication: CWDM technology is widely used in telecommunication networks to increase the capacity and efficiency of data transmission.
- Enterprise Networks: It is employed in enterprise networks for connecting multiple locations and data centers.
- Broadcasting: CWDM Mux/Demux facilitates the transmission of high-definition video and audio signals in broadcasting applications.
In conclusion, CWDM Mux/Demux plays a crucial role in optimizing optical fiber communication networks by enabling the efficient multiplexing and demultiplexing of optical signals. Its cost-effectiveness and simplicity make it a preferred choice for various applications requiring increased bandwidth and streamlined network architecture.